Poster | 6th Internet World Congress for Biomedical Sciences |
Francisca Mulero(1), J.A. Ruiz-Ros(2), F. Martinez-Corbalan(3), F. Picó(4), J.A. Nuño de la Rosa(5)
(1)(2)(5)Hospital Universitario Virgen de la Arrixaca - San Miguel de Salinas. Spain
(3)(4)Servicio de Medicina Nuclear. Hospital Universitario Virgen de la Arrixaca - Murcia. Spain
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Genetics & Bioinformatics] |
[Radiology & Nuclear Medicine] |
21 out of 24 Syndrome X patients showed a normal pattern in the slices studies and polar maps; 3 patients showed a slight defects. Interestingly, those 21 patients with normal slices studies and polar maps also showed abnormal washouts. The patients that showed normal washouts, also had normal slices studies and polar maps.
PATIENTS WITH SYNDROME X AND CONTROLS DATA
* Statistical analysis (t de Student ). Syndrome X versus controls
| THALLIUM SCANS | Syndrome X | Controls | p Value* |
| Mean stress counts | 83.72 ± 4 | 111.99 | < 0.05 |
| Mean redist counts | 86.22 ± 4 | 108.13 | < 0.05 |
| Washout | -3.11 ± 2.27 | 3.44 | < 0.05 |
| CLINICAL DATA | Ergometric characteristics |
| ST depression (mm) | 1.9 ± 0.6 |
| HR at max. ST depression | 135.2 ± 19.1 |
| Time ST depression | 278.5 ± 182.2 |
| HR at 1 mm ST depression | 124.8 ± 19.1 |
| Time 1 mm ST depression | 261.2 ± 205.4 |
| HR x SBP | 26641 ± 4017 |
| METZs | 7.2 ± 2.9 |
| Post-Exercise ST Recuperation time | 160.0 ± 153.7 |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 192.1 ± 21.7 |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 89.6 ± 11.2 |
( DBP: Diastolic blood pressure; HR: Heart rate b/min; METZs: Metabolic equivalents;
SBP: Systolic blood pressure; Time: seconds ).
Syndrome X patients showed a significant reduction in Thallium 201 uptake at periods of peak exercise compared to the uptake shown by control subjects (83.72 vs 111.99; p < 0.05). Redistribution results show that Syndrome X patients have a higher Tallium uptake in resting periods than after exercise, whereas control individuals show lower values at rest than after excercise (86.22 patients, vs 108.13 controls; p < 0.05). Washout values are clearly reduced in syndrome X patients as compared to normal subjects (-3.10 vs 3.44; p < 0.05).
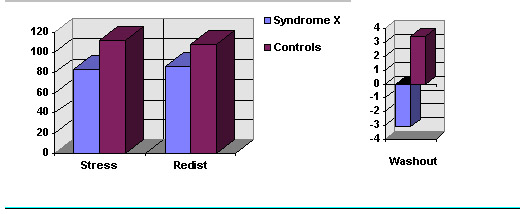
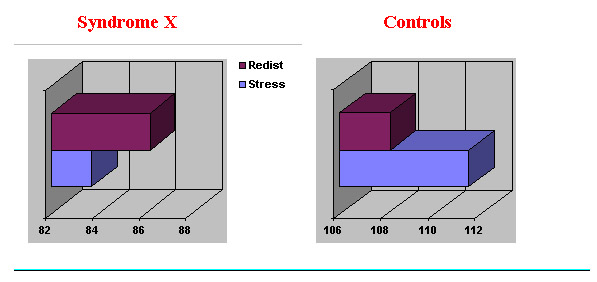
In control subjects, Thallium uptake at rest was reduced a 3,57 % as compared to uptake during exercise. However, Syndrome X patients showed an increase of 3,01% in Thallium uptake as compared to uptake during exercise.
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Genetics & Bioinformatics] |
[Radiology & Nuclear Medicine] |