Poster | 6th Internet World Congress for Biomedical Sciences |
Eiichi Yagi(1)
(1)Akita Red Cross Hospital - Akita. Japan
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Dermatology] |
[Health Informatics] |
Simple growth
Figure 2
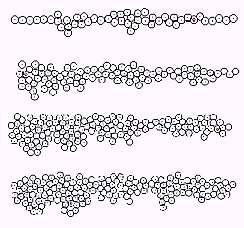
When the growth rate of surroundings cells selected for growth was increased, the rete ridge like structure of was made (Fig. 2). Rete ridge seemed to be longer when the division probability of the basal layer increased.
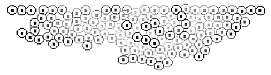
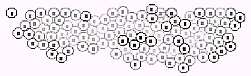
Applied case of growth
P (growth factor) and Q (Inhibition factor) were put in cells according to Turing method. Concentration (P) was displayed by the darkness of cell when R (diffusion rate) was regulated appropriately. The cells, which were with high concentration and near to basal layer, were divided with precedence.
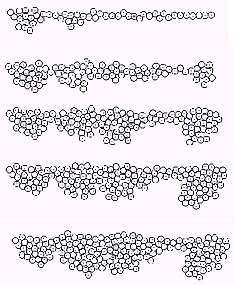
Figure 3

By setting of coefficients, P (growth factor) was arranged in layered formation. Virtual epidermis tends to thicken according to the increase of P (Fig 3). P was able to move toward outside by another coefficient setting. Dilatation speed of eruption was controlled with the balance of P, Q and R.
Cases of proliferation
The switch controlling the proliferation in the lower part of basal layer was set by P, Q factor and the division frequency. Then the structure as a hair root was made (Fig. 5).
A difference of cell size was set large, and a division position was set over the basal layer. It showed like atypicality in situ (in the epidermis)(Fig. 6). Fractal dimension of circumference borderline increases as the probability of difference of cell size rises.
When the division directionality and the adherence to circumference of virtual cell are regulated, a cyst-like structure is constructed (Fig. 7). Keratinization can be done from upward of the tumor. When the direction or speed of the initial keratinization is in a certain range, the structure may be destructed and absorbed immediately.
Cases of proliferation -- addition of horny and granular layer
Virtual granular layer (differentiation stage) is added (Fig. 8), and keratinization is occurred in random position. Virtual granule cells are shown as oval cells, and horny cells are shown as light blued oval cells.
Increase of keratinization tendency and difference of size are added (Fig. 9).
Addition of the randomized differentiation phase and the difference of size (Fig. 10)
Addition of virtual infiltrate cell (Fig. 11)
Similar structure as subcorneal abscess can be made by this option. Implantation of acceleration / inhibiting factor of proliferation in this cell is possible.
By using this growth model the relationship between the arrangement of cellular level and the mass/fractal dimension of structure and the configuration dimension of macro-construction can be examined. If z-axis is added to the functions, the extension to three-dimensional structure is possible. However, the computation time may become enormous.
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Dermatology] |
[Health Informatics] |