dimension of
the circumference
in virtual tumor
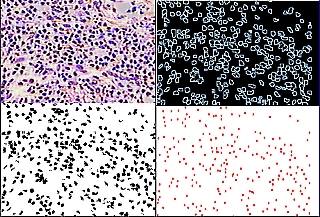
| Distance between cells | Size of nucleus | A length / area of circumference | Concentration difference of nucleus | |
| normal skin | 6.1 | 3.31 | 6.0 | 5.92 |
| seborrheic keratosis | 5.1 | 4.3 | 5.82 | 5.34 |
| actinic keratosis | 5.0 | 2.61 | 6.4 | 4.2 |
| Bowen disease | 5.0 | 1.42 | 6.75 | 4.02 |
| squamous cell carcinoma | 4.9 | 0.85 | 7.87 | 6.15 |
| basal cell cancer | 5.2 | 1.35 | 6.67 | 1.74 |
| Paget disease | 4.6 | 2.65 | 7.4 | 3.1 |
| dermatofibroma | 4.84 | 2.6 | 7.68 | 6.88 |
| hemangioma | 3.6 | 2.22 | 6.8 | 7.9 |
| pigmented nevus | 6.05 | 3.0 | 6.16 | 6.2 |
| Simple fractal dimension of the circumference in virtual tumor |

|
| Probability of the cell size change at one division of cell (0 to 0.9) |
In order to bring the character of virtual tumor close to the real tumor the coincidence of these dimensions is necessary. Coincidence within a small range may be possible, although a lot of computation process is necessary even in such accordance. If various kinds of algorithms (Genetic Algorithms, serious inquiry method etc.) are used and applied appropriately to choose the functions and coefficients, the examination of character with spreading of cells may be possible.