Presentation | 6th Internet World Congress for Biomedical Sciences |
Albert Sun(1), Bozena Draczynska-Lusiak(2), Grace Sun(3)
(1)(2)(3)Department of Pharmacology. University of Missouri - Columbia. United States
|
|
|
|
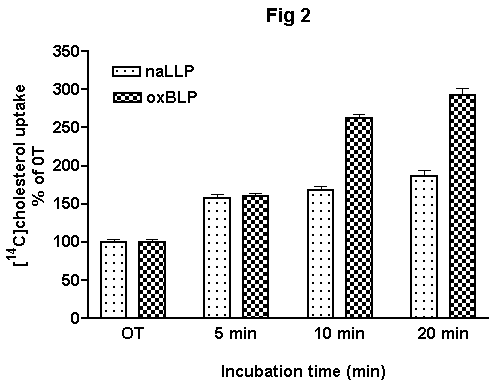 |
| Fig 2. Time course of uptake of BLPs labeled with |
|
|
|
|