Presentation | 6th Internet World Congress for Biomedical Sciences |
Xing Fan(1), Lourdes Gómez(2), Angel Pestaña(3), Luis Santamaría(4), Manuel Nistal(5), Javier Saez Castresana(6)
(1)Department of Genetics. University of Navarre - Pamplona. Spain
(2)Department of Genetics. University of Navarra - Pamplona . Spain
(3)Instituto de Investigaciones Biomedicas, CSIC - Madrid. Spain
(4)Department of Morphology (Histology) . Universidad Autonoma de Madrid (UAM) - Madrid. Spain
(5)Department of Morphology (Histology). Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (UAM) - Madrid . Spain
(6)Departamento de Genetica. Universidad de Navarra - Pamplona. Spain
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
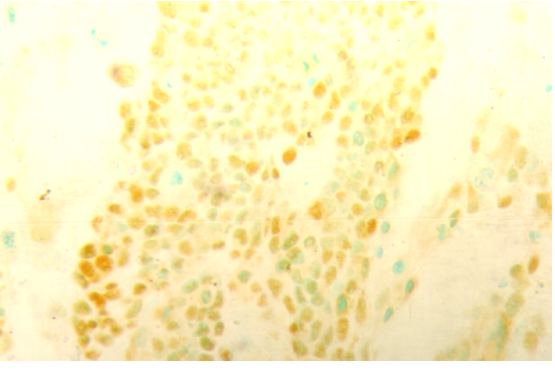
Fig. 1: Indifferentiated Neuroblastoma. Positive immunostaining for p53 (3+): general staining in the cellular nuclei (X40).
|
 |
|
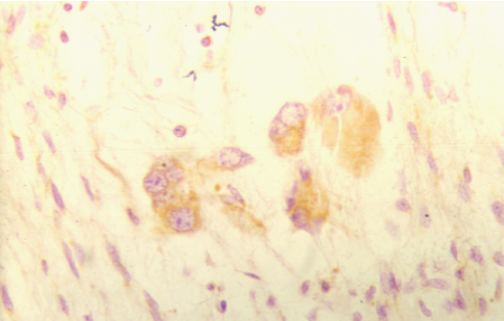
Figuras 2: Ganglioneuroblastomas. Positive immunostaining for p53. p53 citoplasmic expression is detected at the ganglionic neuron cells. Counter stained with hematoxylin (X40).
|
 |
|
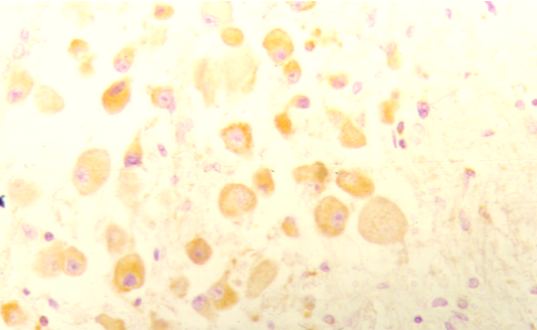
Figuras 3: Ganglioneuroblastomas. Positive immunostaining for p53. p53 citoplasmic expression is detected at the ganglionic neuron cells. Counter stained with hematoxylin (X40).
|
 |
|
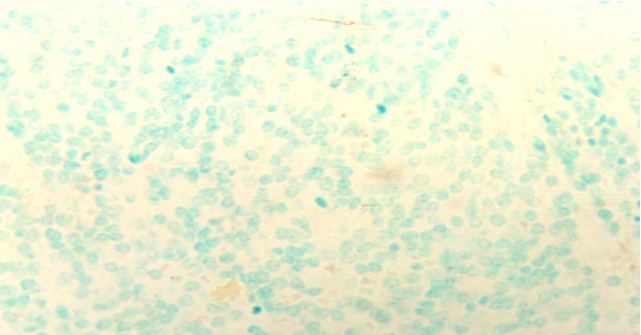
Fig. 4: Indifferentiated Neuroblastoma. Negative immunostaining for p53. Counter stained with methyl green (X40).
|
 |
|
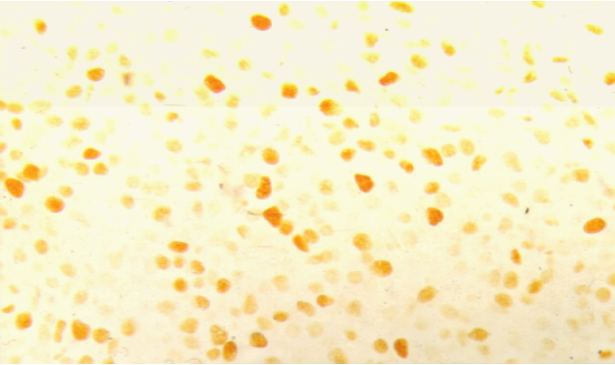
Fig. 5: Indifferentiated Neuroblastoma. Positive immunostaining for PCNA (3+): general staining in the cellular nuclei (X40).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|