|
NEW CONCEPTS AND PERSPECTIVES IN DCIS AND LCIS OF THE BREAST
Prof.
Giovannino Massarelli
Instituto de Anatomía Patológica
Universidad de Sassari, Italia
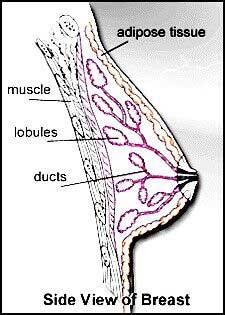
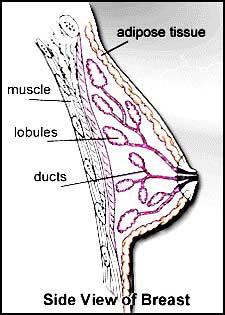
- Normal Breast Structure .
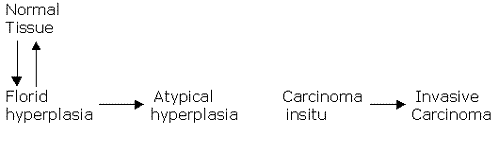
DCIS and LCIS of the breast-Chain
of events:
- DCIS and LCIS of the breast: Common questions:
- Are DCIS and LCIS two clinically distinct forms?
- Are DCIS and LCIS homogeneous conditions?
- Which is the risk of transformation into invasive cancer?
- Which type of cancer does develop?
- Which could be the best rational therapeutic approach?
Top
- DCIS and LCIS of the breast: Objectives
of the presentation
- Definition
- Prevalence
- Classification
- Histology & Immunophenotype
- Site and cell of origin
- Genotype and hormonal profile
- Therapeutic procedures
- DCIS and LCIS of the breast: Definition
- Proliferation of neoplastic epithelial cells within ducts (DCIS)
or lobules (LCIS)
- Cells are still surrounded by an intact basal membrane and/or
by a rim of myoepithelial cells
- Cells show variable degrees of atypia or anaplasia
- DCIS and LCIS of the breast: Definition
Proliferation of neoplastic epithelial cells within ducts (DCIS)
(Figure 2) or lobules (LCIS) (Figure 3)
Figure 2
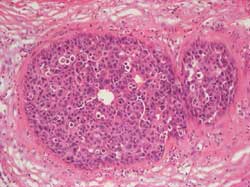
Figure 3
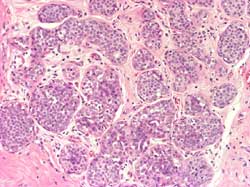
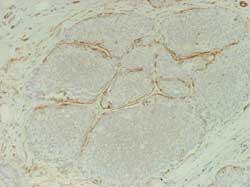
Cells are still surrounded by an intact basal membrane and by a
rim of myoepithelial cells (Figure 4)
Figure 4
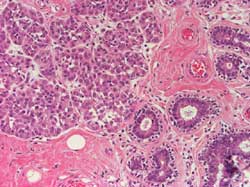
Cells show variable degrees of atypia or anaplasia (Figure 5)
Figure 5
- DCIS and LCIS of the breast: Prevalence1
Before 1980
- 1.4 % of all breast biopsies (LCIS 0.6%)
- Less that 5% of all breast carcinomas
- LCIS:DCIS = 3:1
Nowadays
- 7.5% of all breast biopsies (LCIS 1.1%)
- 40% of all breast carcinomas (LCIS 5.7%)
- DCIS:LCIS = 5:1
Top
- DCIS and LCIS of the breast: Main difference1
DCIS
- Usually monofocal and monolateral
- Lymph node metastases in about 4% of cases
- 90 % into invasive ductal carcinoma within 5 ys of diagnosis
- Relapses in the original breast
- Is considered a precancerous lesion
LCIS
- Usually multifocal and bilateral (from 50 to 100%)
- Lymph node metastases in less than 1% of cases
- 60% into invasive lobular or ductal carcinoma within 15-20
ys of diagnosis
- May relapse in contralateral breast (same risk as in ipsilateral
breast)
- Is considered a risk factor (RR 9-12-folds)
- DCIS of the breast: Classification2
- Well differentiated
- Intermediately differentiated
- Poorly differentiated
- DCIS of the breast: Histology2
Well differentiated: Composed of cells with monomorphic
nuclei and architectural differentiation into cribriform, micropapillary
or clinging patterns. Necrosis is absent and cells may show some
secretory appearance. There are usually psammomatous calcifications.
Solid growth pattern may be present but cells are small and polarized
(Figure 6 and 7)
Figure 6
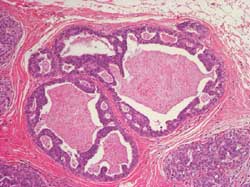
Figure 7
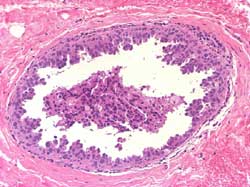
Intermediately differentiated: Composed of cells with pleomorphic
nuclei with moderate variation in shape and size without architectural
differentiation. Necrosis and calcifications may be variable; these
latter are amorphous or psammomatous (Figure 8)
Figure 8
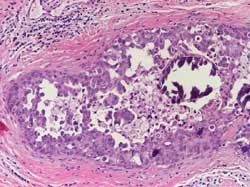
Poorly differentiated: Composed of cells with markedly pleomorphic
nuclei, evidence of individual cell necrosis and autophagocytosis.
Mitoses are present. The growth pattern may be solid, pseudopapillary,
pseudocribriform, and usually with central necrosis that often contains
amorphous calcifications (Figure 9)
Figure 9
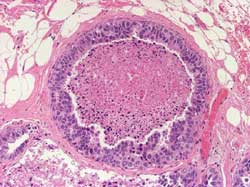
- CLIS of the breast: Classification3
- Small cell (classic) or Type 1
- Large cell or Type 2
- Signet ring cell or Type 3
- CLIS of the breast: Histology3
Small cell (classic): Lobules are enlarged by a monomorphous
cell proliferation; association with ALH; no pagetoid spreading
(Figure 10)
Figure 10
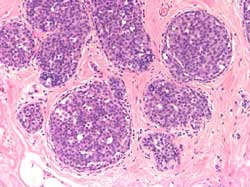
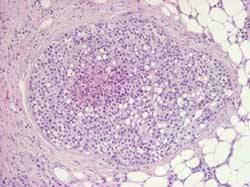
Large cell: proliferation of large uncohesive
cells usually displaying a pagetoid spreading. Frequently evolves
into or is associated with invasive lobular carcinoma (Figure 11)
Figure 11
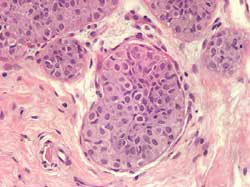
Signet ring cell: proliferation of small or large cells with
intracytoplasmic lumina containing Alcian or PAS positive mucins.
Frequently evolves into or is associated with invasive ductal carcinoma
(Figure 12)
Figure 12
Terminal Duct LobularUnit: (Figure 13)
Figure 13
Top
- DCIS and LCIS of the breast: Interpretation4
|
DIN
|
LIN
|
MIN (hybrid)
|
| 1a (IDH) |
LIN 1 (ALH) |
LCIS + IDC |
| 1b (clinging) |
LIN 2 (Type 1) |
|
| 1c (ADH/low malig.) |
LIN 3 (Type 2/3) |
|
| 2 (interm. malig.) |
3 (high malig) |
|
- LIN is considered a relatively unstable state of cancer progression
- DCIS and LCIS of the breast: E-cadherin and HMW CK expression4
|
DCIS
|
LCIS
|
| E-cadherin + |
E-cadherin - |
| HMW CK (34bE12) + |
HMW CK (34bE12) - |
but
DCIS high grade retains the ability to express e-cadherin and loses
that to express HMW CK, whereas LCIS type 2 and 3 may express HMW
CK in perinuclear capping.
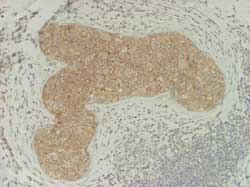
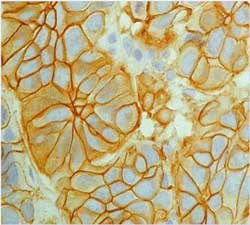
- DCIS and LCIS of the breast: E-cadherin
DCIS: (Figure 14)
Figure 14
LCIS: (Figure 15)
Figure 15
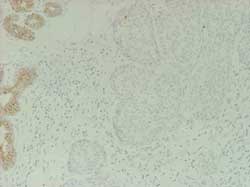
DCIS and LCIS of the breast: Cell proliferation, hormone receptors,oncogene
and tumor suppressor gene expression5
| Taking into account
that |
low MIB1 index correlates
with
high ER and PR values and
no expression of c-erbB-2 and p53 |
DCIS low grade and LCIS (all types) share the same profile
but
the inverse correlation occurs leading from DCIS intermediate to
high grade malignancy. A similar pattern may be observed in infiltrating
lobular carcinoma, pleomorphic.
P53 expression (Figure 16)
Figure 16
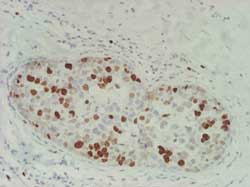
ER expression (Figure 17)
Figure 17
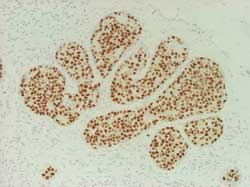
Score 2+ (Figure 18)
Figure 18
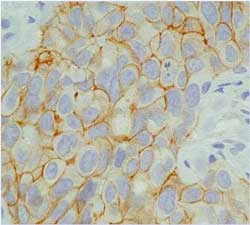
Score 3+ (Figure 19)
Figure 19
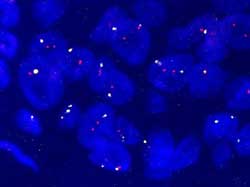
R/G=1,2 (Figure 20)
Figure 20
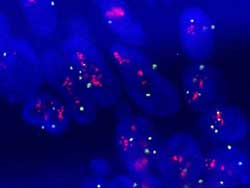
R/G=5 (Figure 21)
Figure 21
Top
DCIS and LCIS of the breast: Genetic alterations
6,7
|
DCIS
|
LCIS
|
| Gains of 8q and
12p |
Gains of 1q |
| Losses of 8p,
13q, 14q, 16q |
Losses of 16q |
* LCIS is not a manifestation of BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations
* Some cases of CLIS show germline mutations in MLH1 but not in
MSH2
DCIS and LCIS of the breast.Proposed therapeutic approach
DCIS
All types: lumpectomy and tamoxifen
LCIS
Type 1: lumpectomy and "wait and watch"
Type 2 and 3: lumpectomy and tamoxifen
- DCIS and LCIS of the breast: Common questions:
- Are DCIS and LCIS two clinically distinct forms?
- Are DCIS and LCIS homogeneous conditions?
- Which is the risk of transformation into invasive cancer?
- Which type of cancer does develop?
- Which could be the best rationale therapeutic approach?
Top
References:
1-Frykberg ER: Breast J, 5:296-302; 1999.
2-Holland R, Peterse JL, Millis RR et al. Semin Diagn Pathol 11:167-180,
1994.
3-Barsky SH, Bose S: Breast J,5: 407-412,1999.
4-Bratthauer GL et al. Human Pathol,33:620-627,2002
5-Rudas M et al. Eur J Cancer 33:39-44,1997.
6-Buerger H et al. J Clin Pathol: Mol Pathol 53:118-121,2000.
7-Stone JG et al: Cancer Letters 167: 171-174,2001.
Top
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|