| Información || Congresos || Cursos || Territoriales || Noticias || Patología || Telepatología |
SEMINARIO DE XCVII REUNIÓN DE LAS ASOCIACIONES TERRITORIALES
DE LA SEAP Y DE PORTUGAL
--------
REUNIÃO DAS INTERDEPARTAMENTAIS DE ANATOMIA PATOLÓGICA
DE PORTUGAL E DO NORTE DE ESPANHA
HOSPITAL DE SÃO JOÃO – PORTO
Apresentado por: Dr.ª Joanne Lopes. Serviço de Anatomia Patológica
Resumen del caso:
A case-report concerning a 50 year old man presenting in November 2003 with hoarseness, dyspnea and dysphagia, high serum levels of calcitonin (947 pg/ml) and CEA (397.2 ng/ml), and normal levels of T3, T4 and TSH. There was no family history of thyroid cancer. A cervical ultrasonography revealed a cervical lymph node measuring 6cm in diameter. Lymph node FNAC showed metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma. In December 2003, the patient was submitted to a total thyroidectomy with bilateral cervical lymph node dissection of the central and lateral compartments. The thyroid weighted 13g and no macroscopic abnormalities were observed. The left lateral compartment consisted on a large lymph node measuring 6cm in diameter. In the central and right lateral compartments, one and 13 lymph nodes were isolated, respectively. The diagnosis of medullary thyroid microcarcinoma (1)(2) measuring 0.2cm of largest diameter was established after microscopic examination of the whole thyroid specimen (fig-1). There was C-cell hyperplasia. The lymph nodes presented extensive metastases. No germline RET mutations were found. In August 2005, the patient presented Cushing's syndrome with high levels of ACTH (113 pg/ml) and CEA (436 ng/ml), and evidence of calcitonin (1.1 pg/ml) in the serum. A CT scan revealed a 2 cm tumor in the left lobe of the liver. A liver core biopsy was performed. Part of the liver tissue was occupied by a tumor with a solid or insular growth pattern, composed of round or polygonal cells with abundant cytoplasm. Many of the cells had large vacuoles containing mucin (PAS and PAS-D positive), assuming a signet-ring cell appearance (fig-2). Since the presence of signet-ring cells usually indicates the possibility of a mucinous tumor of gastrointestinal origin (3)(4), immunohistochemical staining was performed. The tumor was positive for NSE, chromogranin, calcitonin and CEA, thus confirming the diagnosis of metastatic medullary carcinoma. Some of the tumor cells were also positive for ACTH. Both carcinoid and Cushing`s syndromes have been reported in patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma, presumably due to the synthesis and secretion of serotonin or related amines and ACTH by the tumor (5).
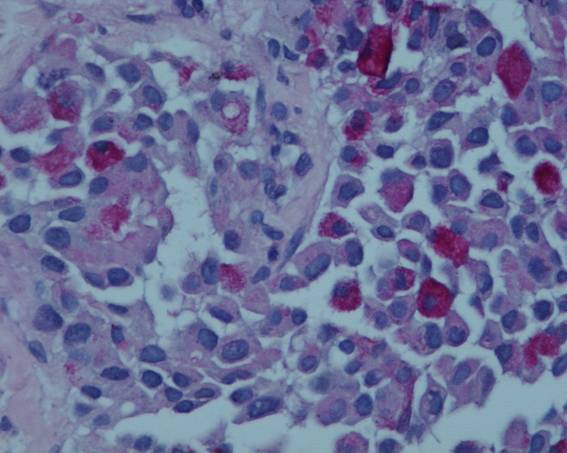
Fig 1. PAS-D
Fig. 2
Metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma with signet- ring cell features.
Metástase hepática de micro-carcinoma medular
Bibliografía.
(1) Guyetant S, Dupre F, Bigorgne JC, Franc B, Dutrieux-Berger N, Lecomte-Houcke M, Patey M, Caillou B, Viennet G, Guerin O, Saint-Andre JP. Medullary thyroid microcarcinoma: a clinicopathologic retrospective study of 38 patients with no prior familial disease. Hum Pathol 1999;30:957-63.
(2) A. DeLellis, Ricardo V. Lloyd, Phillip U. Heitz, Charis Eng. WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs. IARC Press: Lyon 2004
(3) Fernandes BJ, Bedard YC, Rosen I. Mucus-producing medullary cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland. Am J Clin Pathol 1982;78:536-40.
(4) Martin-Lacave I, Gonzales-Campora R, Moreno-Fernandez A, Sanchez-Gallego F, Montero C, Galera-Davidson H. Mucosubstances in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. Histopathol 1988; 13:55 -66.
(5) Morales AM, Horn RC. Thyroid carcinoma and Cushing`s syndrome. A report of two cases with a review of the common features of the non-endocrine tumors associated with Cushing`s syndrome. J Clin Pathol 1968;21:129-35.
Última actualización: 20 de marzo de 2006